- Home»
- News»
- All News Articles»
- New Development Platforms
18 Feb 12
STMicroelectronics has come up with a new method for data storage with a dual-interface wireless EEPROM memory IC, the M24LR16E.
This device can operate normally with a standard low power I2C interface or it can switch over to a 13.56-MHz ISO15693 contactless RF interface for wireless communication.
The antenna used for the two-way data transfer in the RF interface mode has a dual purpose. Beyond transfering data, its second purpose is to harvest ambient energy in the RF signal being transmitted, and use that to supply its own power, and convert the excess into a voltage output that may be used to power other electronic components.
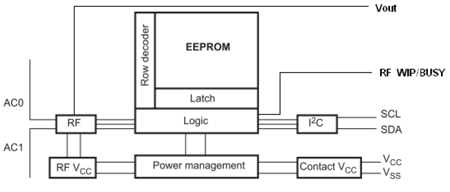
While operating in the RF energy harvesting mode and I2C disabled, an entire low-power system can be powered directly from harvested RF energy. No battery or external power supply would be required for this, since no power would be needed on the Vcc pin. In case the RF field strength is insufficient or when the energy harvesting mode is disabled, the analog output pin Vout goes into high-Z state and the energy harvesting mode is automatically stopped.
Using this device would simplify the development and maintenance of many applications, as the need for batteries, power cables, and data lines is eliminated. This would have potential for many new applications, as new designs can be much smaller and lighter, and much less expensive. It is possible for a system to become virtually maintenance-free by using this method.
Some of the potential applications would include e-paper devices such as electronic shelf labels, sensing and monitoring systems, industrial automation, and personal healthcare products. It is anticipated that this type of device would be widely used in RFID/NFC-compatible devices as RFID is becoming standardized in supply-chain and retail businesses. NFC technology is another possibility, as it is estimated to be used in more than 500 million mobile phones sold annually by 2015.
The power management circuitry integrated in the M24LR16E makes the extra harvested energy available to other devices on the board through an output pin. The nominal output voltage output on this pin is between 1.7 and 2.3V, which is sufficient to power a few low-power ICs, such as CMOS chips. The maximum output current on this pin can be configured from 300µA to 6mA by setting bits in an internal register.
The M24LR16E-R also features a user configurable digital out pin (RF WIP/BUSY) that can be used to drive a micro controller interrupt input pin. This pin is activated only when power is applied to the Vcc pin, and can be set to toggle for RF write in progress, or RF busy (command in progress), depending on the mode selected.
The EEPROM memory in the M24LR16E is 16Kbits, and it is organized as 2048 x 8 bits in the I2C mode and 512 x 32 bits in the ISO 15693 and ISO 18000-3 mode 1 RF mode.
The memory device includes a data protection scheme to protect stored data against threats such as accidental over-writing and unauthorized access or tampering. There are several password protection options included, up to 32 bits.
The device operates at a 1.8V to 5.5V supply-voltage range and is available in SO8, TSSOP8 or MLP8 surface-mount packages. The antenna required for wireless operation can simply be etched on the printed circuit board.
